Arrays in JavaScript
Overview
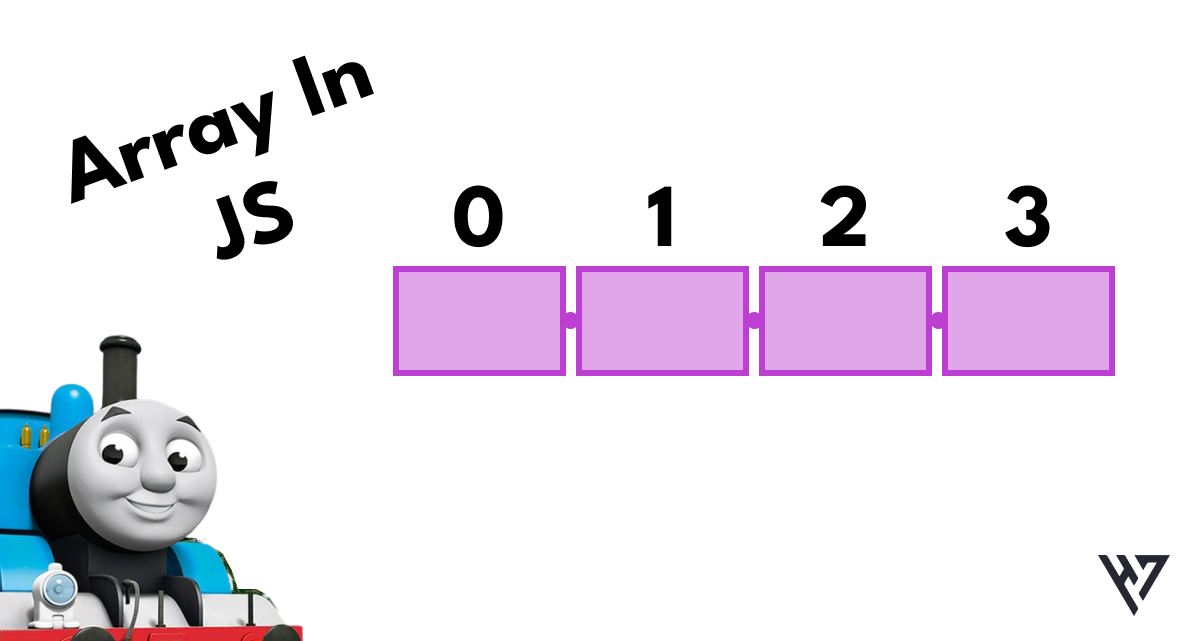
An array is a fundamental data structure in JavaScript, used to store and organize multiple values in a single variable. It is a collection of elements, each identified by an index or a numeric position, starting from 0. Arrays can hold elements of any data type, including numbers, strings, objects, and even other arrays, making them versatile and powerful for handling various types of data.
In JavaScript, arrays are declared using square brackets []. Elements are separated by commas. Here’s an example of an array containing a few elements:
let fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape'];
console.log(fruits);
// output: [ 'apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape' ]You can access individual elements of an array using their index, which is a zero-based integer value.
push
When we are working with an array we need to push values at end to array we can use array.push("value")
fruits.push('new fruit');
console.log(fruits);
// output: [ 'apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape', 'new fruit' ]Time Complexity is O(1) because we adding value at end array
remove last value
To remove last value we can use array.pop()
fruits.pop();
console.log(fruits);
// output: [ 'apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape']Time Complexity is O(1) because we removing value at end array
adding at start
add a value at the start of array we can use array.unshift(value)
fruits.unshift('new Value');
console.log(fruits);
// output: [ 'new Value', 'apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape' ]Time Complexity is O(N) because we adding value at start array
adding in-between
To add value in between we can use splice array.splice(index, delete_count, new_value)
fruits.splice(2, 0, 'new Value');
console.log(fruits);
// output: [ 'apple', 'banana', 'new Value', 'orange', 'grape' ]Time Complexity is O(N) because we adding value in-between array
spread syntax in arrays?
In JavaScript, the spread syntax is a powerful feature that allows you to expand elements from an array or an iterable object into another array or function arguments. It is denoted by the three dots … The spread syntax is particularly useful for making copies of arrays, combining arrays, and passing multiple arguments to functions in a concise and efficient way.
To use the spread syntax with arrays, you can apply it in the following scenarios:
Copying an array:
You can easily create a new copy of an existing array by using the spread syntax. This operation creates a shallow copy, meaning that nested objects or arrays within the original array are still referenced rather than cloned.
const originalArray = [1, 2, 3];
const copiedArray = [...originalArray];
console.log(copiedArray);
// Output: [1, 2, 3]Time Complexity is O(N) because we have travel whole array
Merging arrays:
You can merge two or more arrays into a single array using the spread syntax. This is a quick and efficient way to combine arrays without modifying the original ones.
const array1 = [1, 2];
const array2 = [3, 4];
const mergedArray = [...array1, ...array2];
console.log(mergedArray);
// Output: [1, 2, 3, 4]Time Complexity is O(M) + O(N) because we have travel both arrays so each
Adding elements to an array:
The spread syntax can be used to add elements to an existing array while keeping its original content intact.
const originalArray = [1, 2, 3];
const newArray = [...originalArray, 4, 5];
console.log(newArray);
// Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]Time Complexity is O(N) because we have travel whole arrays so each
Passing multiple arguments to a function:
When calling a function, you can use the spread syntax to pass elements of an array as separate arguments to the function.
function sum(a, b, c) {
return a + b + c;
}
const numbers = [1, 2, 3];
const result = sum(...numbers);
console.log(result);
// Output: 6The spread syntax is a powerful and versatile feature in JavaScript, and it greatly simplifies working with arrays. It helps in creating copies, merging arrays, and making function calls with multiple arguments, providing a more concise and expressive way to manipulate and work with arrays in your code.